History of endoscopic ultrasonography(EUS)
History of endoscopic ultrasound
History of echo-endoscopy
Please see "History of Echocardiography" Click here
Timeline of the progress in endoscopic ultrasonography

If you have time, please see "Timeline of the development of EUS and TEE". Click here
Please see "History of Echocardiography". Click here
Another timeline and references
1976 Lutz H et al. Transgastric A-mode echo. (ref.1) A-mode only. A-mode is not used now.
1977 Hisanaga K et al. Transesophageal 2D sector scanner using a flexible tube. (ref.2, ref.5)
Human examination.
1978 Hisanaga K et al. Endoscopic ultrasonography. Transgastric sector scanner with a flexible
gastrofiberscope. (ref.3, ref.4, ref.10) Human examination. Optic guidance. The first transgastric
ultrasound scanner (EUS) with a fiberscope in history. Small transducer with long wire that can insert into the forceps hole of a gastrofiberscope.
1978 Hisanaga K et al. Transesophageal ultrasound linear scanner. (ref.7, ref.19)
1979 Hisanaga K et al. EUS, Transgastric high speed rotating scanner using a flexible tube.
(ref.11, ref.12, ref.14, ref.15, ref.16, ref.17) Human examination. Image of pancreas.
This is the first transgastric high speed ultrasound scanner(EUS)in history.
1979 Hisanaga K et al. Transesophageal high speed rotating scanner using a flexible tube.
(ref.9, ref.12, ref.18, ref.23) Human examination.
1980 Hisanaga K et al. Filling stomach with water method in EUS examination (ref.20,ref.21, ref.22, ref.29)
Very important method in EUS examination.
1980 Dimagno EP et al. Linear EUS. (ref.13) Animal (Dog).
1980 Strohm WD et al. Transgastric ultrasound sector scanner using a rotating mirror with a fiberscope by Olympus. (ref.24, ref.29A) Examination of human. Optic guidance.
1980 Fukuda M et al. Transgastric ultrasound sector scanner using a rotating mirror with
a fiberscope by Olympus. (ref.25) Human examination. Optic guidance.
1981 Aibe T et al. EUS (Rotating mirror system with a fiberscope by Olympus) (ref.26) Optic guidance. Human examination.
1981 Hoshi O et al. EUS (Rotating mirror system with a fiberscope by Olympus). (ref.27) Optic guidance. Human examination.
1981 Yamanaka T et al. Linear array EUS with a fiberscope by Toshiba. (ref.28, ref.33)
Human. Optic guidance.
1982 Souquet J et al. Transesophageal phased array sector scanner. (ref.30, ref.31)
1982 Aibe T et al. Transgastric rotating transducer scanner with a fiberscope. Without rotating mirror.
(ref. 34) Human. Optic guidance.
1982 Lux G et al. Endoscopic ultrasonography by Olympus system. (ref.34A)
1982 Dimagno EP et al. Linear EUS. (ref.35) Human examination. One year after Yamanaka.
1983 Lutz H et al. Transgastric images of pancreas by Linear and sector scanners. (ref.35A)
1984 Yasuda K et al. Endoscopic ultrasonography in pancreatic cancer. (ref.35B)
1989 Hashimoto H et al. Three-dimensional display of gastric tumor by endoscopic
ultrasonography. (ref. 36)
1989 Silverstein FE et al. Very thin catheter type scanner that can be passed through the forceps hole of a
gastrofibersope. (ref.36A) Vertical linear array.
1990 Rosch T et al. Very small catheter type scanner that can be passed through the forceps hole of a
gastrofiberscope. (ref.37) Rotating scanner.
1991 Vilmann P et al. Endoscopic ultrasound. Curved linear-array transducer. (ref.38)
1992 Vilmann P et al. Endoscopic ultrasonography guided fine needle aspiration biopsy in pancreatic
disease. (ref.39)
1992 Van Dam J et al. Endoscopic ultrasonography guided needle aspiration biopsy for the diagnosis of
upper gastrointestinal tract foregut cysts. (ref.40)
1993 Wiersema MJ et al. Endoscopic ultrasonography guided fine-needle aspiration biopsy. (ref.41)
1995 Kallimanis G et al. Three-dimensional endoscopic ultrasonography. (ref.42)
1996 Tano S et al. Diagnosis of pancreatic arteriovenous malformation by endoscopic color Doppler
ultrasonography, (ref.43)
1998 Hirooka Y et al. Contrast-enhanced endoscopic ultrasonography in pancreatic diseases. (ref.44)
2001 Becker D et al. Diagnosis of pancreatic disease by color Doppler endoscopic ultrasound. (ref.45)
2002 Michelle A et al. Electronic radial array echoendoscope. (ref.46)
Anybody can reproduce photographies from this website without permission of Hisanaga.
E-mail correspondence busuchan1122@yahoo.co.jp
References
1. Lutz H, Losch W. Transgastroscopic ultrasonography. Endoscopy 8:203-205, 1976 Note: Not 2-D but A-mode
2. Hisanaga K, Hisanaga A, Nagata K, Yoshida S. A new transesophageal real time two-dimensional echocardiographic system using a flexible tube and its clinical application. Proceedings of the Japan Society of Ultrasonics in Medicine 32:43-44, 1977

From ref.2 Transesophageal horizontal scan in a normal adult.

Kohzoh Hisanaga, MD. (Hisanaga K) From "People who developed medical ultrasound". p35, Itoh K, Ed., Supplement of Proceedings of 60th Meeting of JSUM 1992. Kohzoh Hisanaga is not only an electronic engineer but also medical doctor.
Dr. Hisanaga received the Honor Award of the Japanese college of cardiology in 1991 because
Dr. Hisanaga developed Transesophageal two-dimensional echocardiography for the first time in history.
3. Hisanaga K, Hisanaga A. A new trans-digestive-tract scanner with a gastrofiberscope. Proceedings of the 23rd Annual Meeting of American Institute of Ultrasound in Medicine. p.108, November, San Diego, 1978 A flexible gastrofiberscope was used. Human examination. Optic guidance.
The first transgastric ultrasound scanner in history.
This system with a gastrofiberscope was same to that of ref.20 or ref.21. Please see ref.20.
4. Hisanaga K, Hisanaga A. A new trans-digestive-tract scanner with a gastrofiberscope. Reflections 4, 221, 1978 Human examination. Optic guidance.
5. Hisanaga K, Hisanaga A. A new real-time sector scanning system of ultra-wide
angle and real-time recording of entire adult cardiac images --Transesophagus and Trans-chest-wall methods --. In: White DN, Lyons AE (eds.) Ultrasound in Medicine Vol.4, New York, Plenum Press pp391-402, 1978

From ref.5 Insertions of transducer to esophagus and transesophageal ultrasound examinations were performed with patients in left lateral position(left). Typical horizontal scan in a normal adult by using transesophageal method(right).

From ref.5 Transthoracic image. A long axis scan in a 31-year-old normal man. Entire heart image is seen. The endocardium of the left ventricle and the right ventricular anterior wall are seen.

From ref.5 Transesophageal M-mode echograms. These images were recorded in order to identify echo sources of transesophageal cross-sectional images shown in Fig.10. Arrows A, B and C of Fig.10A and Fig.10D correspond to Fig.9A, 9B and 9C in each and show directions of M-mode echograms.
6. Hisanaga K, Hisanaga A, Nagata K, Ichie Y, Yoshida S. Transesophageal cross- sectional echocardiography --New method for cardiac diagnosis--. (abstr.) Jp Circulation J (Circulation Journal) 42:773, 1978
7. Hisanaga K, Hisanaga A, Nagata K, Ichie Y, Yoshida S. A new transesophageal high
speed linear scanner and its clinical application. Proceedings of the Japan Society of Ultrasonics in Medicine 33:47-48, 1978

From ref.7 Transesophageal vertical scan through mitral valve in a normal adult.
8. Hisanaga K, Hisanaga A, Ichie Y. A transesophageal ultrasound sector scanner
for oblique scan. (abstr.) Circulation 60(suppl. II): II-245, 1979
9. Hisanaga K, Hisanaga A, Nagata K, Ichie Y. Cardiac imaging using a ultrasound high
speed rotating scanner. Proceedings of the Japan Society of Ultrasoics in Medicine 35:157- 158, 1979
10. Hisanaga K, Hisanaga A, Nagata K, Ichie Y. A trans-stomach wall sector scanner
with a gastrofiberscope. Abstract of 2nd WFUMB, p383, July 22-27, Miyazaki, 1979
A flexible gastrofiberscope was used. Examination of human, optic guidance. Abstract with images. This system with a gastrofiberscope was same to that of ref.20 or ref.21.
Please see ref.20.
11. Hisanaga K, Hisanaga A, Nagata K, Ichie Y. A trans- stomach wall high speed
rotating scanner and initial clinical results. Proceedings of the Japan Society of Ultrasoics in Medicine 35:115-116, 1979 A flexible tube was used. This is the first full paper of transgastric ultrasound scanner (EUS) in history. Human.
Paper of a new EUS system (Transgastric high speed ultrasonic rotating scanner)

Photography of the original paper.

From ref.11 Trans-stomach-wall high speed rotating scanner.

From ref.11 Horizontal scan through the left kidney in a normal adult by using the trans-stomach-wall rotating scanner. When near gain is standard, pancreas is seen as echo free space near the stomach.
From ref.11 Horizontal scan through the left kidney in a normal adult by using the trans-stomach-wall rotating scanner. When near gain is standard, pancreas is seen as echo free space near the stomach.
12. Hisanaga K, Hisanaga A. High speed rotating and sector scanners for transesophageal echocardiography and transgastric sonography. (in Japanese) Eizou Jouhou Medical 11:1094-1099, 1979 Flexible tube was used.

From ref.12 Transgastric high speed rotating scanner with a flexible tube.

From ref.12 Fig.11 Horizontal scan at the level of kidney in a normal adult. Pancreas is seen very clearly.
13. Dimagno EP, Regan PT, Wilson DA, Buxton JL, Hattery RR, Suarez JR, Green PS.
Ultrasonic endoscope. Lancet 1:629-631, 1980. Note: not human but animal(dog)
14. Hisanaga K, Hisanaga A, Nagata K, Ichie Y, Kambe T. Trans-stomach-wall
cross-sectional echography -examination technique and identifications of abdominal cross-sectional images-. Proceedings of the Japan Society of Ultrasoics in Medicine 36:131-132, 1980 Flexible tube was used.

From 14. Fig.2 Trans-stomach-wall cross-sectional echogram including vertebra. (panel A)
Trans-stomach-wall cross-sectional echogram including spleen (panel B). Spleen is seen clearly in panel B. SW = stomach wall, F = foramen vertebra, LK = left kidney, AA = abdominal aorta, R = right, L = left.
15. Hisanaga K, Hisanaga A. Pancreatic echography using a trans-stomach wall
ultrasound rotating scanner. (abstr) Gastroenterology 78:1183, 1980
Examination of human.
16. Hisanaga K, Hisanaga A, Kambe T. An endoscopic ultrasound scanner for abdominal echography. (abstr) Gastrointestinal Endoscopy 26:68, 1980 Examination of human.
17. Hisanaga K, Hisanaga A, Nagata K, Ichie Y. High speed rotating scanner for
transgastric sonography. Am J Roentgenol 135:627-629, 1980 A flexible tube was used. Image of pancreas.

From ref.17 Upper Fig. Intragastric high speed rotating scanner. Small transducer in stomach is rotated by flexible rotating shaft and motor at 15-50 cycles/sec. Lower Fig. Transducer and commutator in oil bag.

A

B Image of pancreas
From ref.17 Horizontal scans through left kidney in a normal adult with intragastric high speed rotating scanner. A: Left kidney and abdominal aorta are seen clearly. If amplitude of near field is relatively low, pancreas is seen as anechoic space near stomach wall. B: With increasing amplitude of near field, pancreas assumes cloudlike shape.
18. Hisanaga K, Hisanaga A, Ichie Y, Hibi N, Nishimura K, Kambe T. High speed rotating
scanner for transesophageal cross-sectional echocardiography. Am J Cardiol 46:837-842, 1980

From ref.18 Diagrammatic illustration of the transesophageal high speed rotating scanner. A small transducer in the esophagus is rotated through a full 360° through a flexible shaft by a motor at 15 to 50 cycles /s. Although the small transducer is rotated with great speed in the patient's esophagus, no damage results because the transducer is safely enveloped in an oil bag.

From ref.18 Transesophageal high speed rotating scanner.

From ref.18 Transducer and commutator in oil bag. Sound energy is coupled to and from the transducer through the slip-ring commutator because of the full 360° rotation of the transducer.
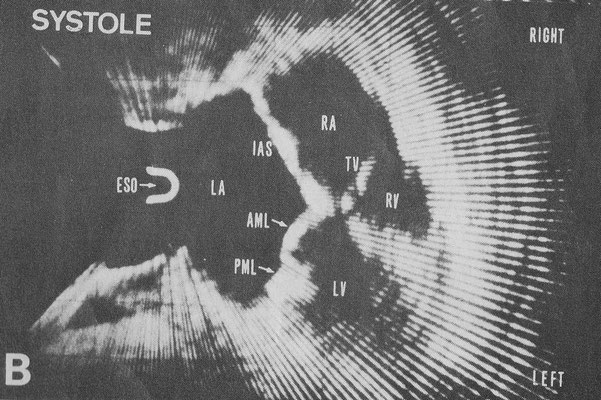
From ref.18 Transesophageal cross-sectional echocardiograms in a patient with mitral stenosis. The cross section is horizontal and shows the heart as viewed from the cardiac apex. A: a frame during diastole and B: a frame during systole. Interatrial septum (IAS) is seen without dropout. AML= anterior mitral leaflet, ESO = esophagus, IVS = interventricular septum, LA = left atrium, LV = left ventricle, PML = posterior mitral leaflet, RA = right atrium,
RV = right ventricle, TV = tricuspid valve.
19. Hisanaga K, Hisanaga A, Nagata K, Ichie Y. Transesophageal cross-sectional
echocardiography. Am Heart J 100:605-609, 1980

From ref.19 Transesophageal horizontal scan at the level of the aortic valve in a patient with mitral stenosis. The aortic cusps are closed in diastole. Large left atrium is seen. Right ventricular outflow tract is seen anterior to the aorta. AV = aortic valve, RVOT = right ventricular outflow tract.

From ref.19 Transesophageal vertical linear scan through the pulmonary artery in a normal subject. Bifurcation of pulmonary artery and part of ascending aorta are seen. AO = aorta, PA = pulmonary artery , BI = bifurcation of pulmonary artery.
From ref.19 Transesophageal vertical linear scan through the pulmonary artery in a normal subject. Bifurcation of pulmonary artery and part of ascending aorta are seen. AO = aorta, PA = pulmonary artery, BI = bifurcation of pulmonary artery.
20. Hisanaga K, Hisanaga A, Kambe T. Transgastric sonography and examination
technique. Proceedings of the Japan Society of Ultrasonics in Medicine 37:413-414, 1980 Paper of the filling stomach with water method

Photography of the original paper.

From ref.20 Fig.2 Transgastric ultrasound sector scanner with a gastrofiberscope.

From ref.20 Fig.12 Horizontal scan through the stomach posterior wall in a normal adult by using the transgastric sector scanner with a gastrofiberscope when the stomach was filled with water. Left kidney is seen clearly. Near gain was very low in order to remove noise rings. SW = stomach wall, LK = left kidney, V = vertebra, R = right, L = left
Content of this paper is the method of filling the stomach with water during EUS examination in order to increase acoustic contact between the stomach wall and transducer. Hisanaga performed this method in 1980.
21. Hisanaga K, Hisanaga A. Endoscopic ultrasound system with an optical fiberscope
and examination technique -filing stomach with water method-. (in Japanese) Eizou Jouhou Medical Vol.12, No.13, pp773-776, August 1980

From ref.21 Fig.1 Diagrammatic illustration of the transgastric ultrasound sector scanner with a gastrofiberscope.

From ref.21 Fig.3 Transducer in stomach when a normal adult drunk water over 300ml.
Comment: There is no dot noise pattern in original photo.

From ref.21 Fig.4 Horizontal scan through the stomach posterior wall in a normal adult by using the transgastric sector scanner with a gastrofiberscope when the normal adult did not drink water.

From ref.21 Fig.5 Horizontal scan through the stomach posterior wall in the same adult by using the transgastric sector scanner with a gastrofiberscope when the adult drunk water over 300ml.
22. Hisanaga K, Hisanaga A, Kambe T. Endoscopic transgastric sonography.
Gendai no Sinryou 22(8): 935-942, 1980 (in Japanese)
23. Hisanaga K, Hisanaga A, Kambe T. Endoscopic ultrasonography: examination technique and abdominal images. Rinshou ME 1(5):525-529, 1980 (in Japanese)
24. Strohm WD, Phillip J, Hagenmuller F, Classen M. Ultrasonic Tomography by means of ultrasonic fiberendoscope. Endoscopy 12:241-244,1980 Transgastric mechanical scanner by Olympus (rotating mirror system). Examination of human. Optic guidance.
25. Fukuda M, Hirata K, Saito K. On the diagnostic use of echoendoscope in abdominal
diseases. Ⅰ Diagnostic experiences with a new type on gastric diseases. Proceedings of the Japan Society of Ultrasonics in Medicine 37:409-410, 1980
Rotating mirror system by Olympus. Human examination. Optic guidance.
26. Aibe T, Esaki T, Sataka M, Amano H, Kawashima M, Nagatomi Y, Harima K, Azuma M,
Maetani N, Ariyama S, Fuji T, Kawamura S, Takemoto T et al. The investigation of the ultrasonic endoscope. Gastroenterol Endosc 23:728-735, 1981 EUS (Rotating mirror system with a gastrofiberscope by Olympus). Optic guidance. Human examination.
27. Hoshi O, Koga K, Fukuda S, Yamakawa T, Miyajima I, Yoshida T, Saito T, Ashizawa S,
Minami K, Takahashi T, Takayama K. Clinical experience with an echoendoscope. Gastroenterological Endoscopy 23(5):721-727, 1981
Human. EUS. Rotating mirror system by Olympus.
28. Yamanaka J et al. Proceedings of the Japan Society of Ultrasonics in Medicine 39:409-410, 1981 Electronic linear array EUS with a fiberscope by Toshiba.
Human examination. Optic guidance. One year before Dimagno.(ref.29)
29. Hisanaga K, Hisanaga A. Transgastric endoscopic ultrasonography. Surgical therapy (Geka Chiryo) Vol.44 No.5, 587-593,1981 (in Japanese)
EUS: Filling stomach with water method.

From ref.29 Fig.9 Horizontal scan through right and left kidneys by the transgastric scanner when stomach was filled with water over 300ml.
From ref.29 Fig.9 Horizontal scan through right and left kidneys by the transgastric scanner when stomach was filled with water over 300ml.
29A. Strohm WD, Jessen K, Phllip J, Classen M Endoscopic ultrasonic tomography of the upper digestive tract. Deutsche Medizinische Wochenschrift 29:106:714-717, May 1981
30. Souquet J, Hanrath P, Ziteli L, Kremer P, Langestein BA, Schulter M. Transesophageal phased array for imaging the heart. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering 29:707-712, 1982 Examination of human.

Jacques Souquet, PhD. From Eugene A Hessel et. al. Evolution of Perioperative Echocardiography. Anesthesia Key.
31. Souquet J. Phased array transducer technology for transesophageal imaging of the heart-current status and future aspects-. In: Hanrath P, Bleifeld W and Souquet J(eds.) Cardiovascular Diagnosis by Ultrasound, Martinus Nijhoff Publishers pp251-259, May 1982
Examination of human.

From ref.31 Mitral valve prolapse.
32. Hisanaga K, Hisanaga A. Transesophageal cross-sectional echocardiography with mechanical scanning system. In: Hanrath P, Bleifeld W and Souquet J (eds.) Cardiovascular Diagnosis by Ultrasound, Martinus Nijhoff Publishers pp239-245, May 1982
The title of this paper is "Transesophageal echocardiography". However the content of this paper includes transgastric ultrasonography.
33. Yamanaka T, Sakai H, Yoshida Y, Kawamoto C, Ueno N, Kumagai M, Horiguchi M, Nagasawa S, Tanaka M, Seki H, Ido K, Kimura K. Ultrasonic endoscopy for the diagnosis of abdominal lesions. Gastroenterological Endoscopy 24:598-607, April 1982
Transgastric electronic linear array endoscopic scanner with a fiberscope by Toshiba. Human examination. Optic guidance.
34. Aibe T, Fuji T, Asagami F, Amano H, Kawashima M, Nagatomi Y, Harima K, Azuma M, Maetani N, Ariyama S, Goto T, Kawaura S, Takemoto T. The investigation of the ultrasonic endoscope (the second report). Gastroenterological endoscopy 24(12):1900-1909, 1982 EUS, transgastric rotating transducer scanner with a fiberscope by Olympus. Without rotating mirror. Human.
34A. Lux G, Heyder N, Lutz H, Demling L. Endoscopic ultrasonography--technique, orientation and diagnostic possibilities. Endoscopy 14:220-225,1982
35. Dimagno EP, Regan PT, James EM, Buxton JL. Human endoscopic ultrasonography. Gastroenterology 83(4): 824-829, November 1982 One year after Yamanaka. (ref.28)
35A. Lutz H, Lux G, Heyder N Transgastric ultrasonography of the pancreas.
Ultrasound in Medicine and Biology 9(5): 503-507, 1983
35B. Yasuda K, Tanaka S et al. Use of endoscopic ultrasonography in small pancreatic
cancer. Scand J Gastroenterol. Supplement 102; 9-17, 01 Jan 1984
36. Hashimoto H, Mitsunaga A et al. Evaluation of endoscopic ultrasonography for
gastric tumors and presentation of three-dimensional display of endoscopic ultrasonography.
Surg Endosc 3(4): 173-181, 1989
36A. Silverstein FE, Martin RW et al. Experimental evaluation of an endoscopic ultrasound
probe: in vitro and in vivo canine studies. Gastroenterology 96:1058-1062, 1989
Very small and thin catheter type scanner that can be passed through the forceps hole of
a gastrofiberscope. Vertical linear scanner. This type scanner was reported in 1978 and
1979 already. (ref.3, ref.4, ref.10)
37. Rosch T, Classen M. A new ultrasonic probe for endosonographic imaging of the
upper GI-tract. Preliminary observations. Endoscopy 22:41-46, 1990 Very small
catheter type scanner that can be passed through the forceps hole of a gastrofiberscope.
Rotating scanner.
38. Vilmann P, Khattar S, Hancke S. Endoscopic ultrasound examination of the upper
gastrointestinal tract using a curved-array transducer: a preliminary report. Surg Endosc
5(2):79-82,1991
39. Vilmann P, Jacobsen GK, Henriksen FW, Hancke S. Endoscopic ultasonography with
guided fine needle aspiration biopsy by pancreatic disease. Gastrointest Endosc 38(2): 172-173, 1992 Transgastric-wall fine needle aspiration biopsy.
40. Van Dam J et al. Endoscopic ultrasonography and endoscopically guided needle aspiration for the diagnosis of upper gastrointestinal tract foregut cysts. Am J Gastroenterol 87(6): 762-765, 1992
41. Wiersema MJ, Kochman ML et al. Real-time endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration of a mediastinal lymph node. Gastrointest Endosc 39(3):429-431, 1993
42. Kallimanis G, Garra BS, Tio TL, Krasner B, Al-Kawas FH, Fleischer DE, Zeman RK,
Nguyen CC, Benjamin SB. The feasibility of three-dimensional endoscopic
ultrasonography: a preliminary report. Gastrointestinal endoscopy 41(3):235-239, 1995
43. Tano S, Ueno N et al. Pancreatic arteriovenous malformation with duodenal ulcer.
Demonstration by color Doppler ultrasonography. Dig Dis Sci 41(6):1232-1237, 1996
Diagnosis by endoscopic color Doppler.
44. Hirooka Y, Goto H et al. Contrast-enhanced endoscopic ultrasonography in
pancreatic diseases: a preliminary study. American Journal of Gastroenterology 9(4):632-
635, 1998
45. Becker D, Strobel D, Benatik T, Hahn EG. Echo-enhanced color-and power Doppler EUS for the discrimination between focal pancreatitis and pancreatic cartinoma. Gastrointest Endosc 53(7):784-789, 2001
46. Michelle A, Anderson MD, James M, Scheiman MD. Initial experience with an electronic radial array echoendoscope: Randomized comparison with a mechanical sector scanning echoendoscope in humans. Gastrointestinal Endoscopy 56(4):573-577, 2002
Hisanaga reported examinations of humans in all papers. Apart from gagging, no serious complications were encountered in all transesophageal and transgastric examinations by Hisanaga. Medical Doctor Hisanaga himself developed all transesophageal and transgastric systems without help of any electric companies or organizations except that of Asako Hisanaga.